Yamaha PW-X, PW-X2, PW-ST, PW-TE, PW-CE nylon gearwheel repair
- The nylon gear of the Yamaha PW engine often breaks down
- Yamaha replacement gear wheels available on Tindie
- PEEK CF30
- Buy Bergquist thermal gap filler pads
- How to replace
- Lubrication
- How to avoid gear overload
- Gearwheel breaks when the crank is blocked
- Save the nylon gear by reducing the maximum motor current
The nylon gear of the Yamaha PW engine often breaks down
 Yamaha PW-X, PW-X2, PW-ST, PW-TE, PW-CE broken gearwheel
Yamaha PW-X, PW-X2, PW-ST, PW-TE, PW-CE broken gearwheel
 Yamaha mid drive motor broken nylon gear
Yamaha mid drive motor broken nylon gear
Some Yamaha mid-drive motors have a design flaw: they contain a nylon gear wheel that cannot withstand the maximum force of the motor. The gear can suddenly break if it is severely overloaded. Repairing is expensive, in some countries you have to buy a new motor that costs around $750. This is a serious problem, because after overload, the gear will definitely break again, so you can keep going this way. That's why I made a replacement gear that you can replace yourself. To know if your gearhweel is compatible: the diameter is 60mm and the thickness is 20mm.
Yamaha replacement gear wheels available on Tindie
Worldwide shipping with tracking.
Shipping to the United States is done from the United States itself.
The gearwheels are precisely milled from PA66 GF30 (glass fiber reinforced polyamide 66). This is stronger than the original Yamaha gearwheel.
Note that 3D printed gearwheels are not strong enough.
The gearwheel is compatible with the following Yamaha motors:
PW-X, PW-X2, PW-ST, PW-TE and PW-CE (NOT for the PW-SE)
Giant motors
Please check if the external dimensions of your broken gearwheel are correct:
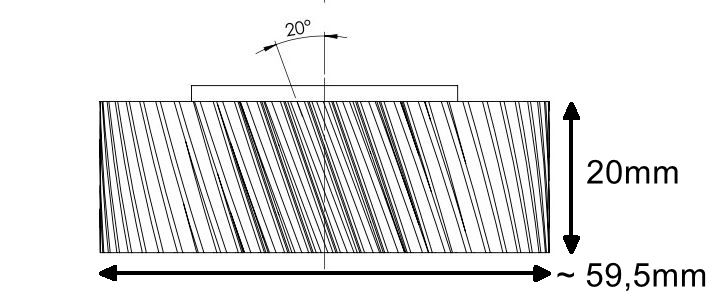 Yamaha PW-series nylon gearwheel dimensions
Yamaha PW-series nylon gearwheel dimensions
PEEK CF30
You can also choose for an extremely strong material: PEEK CF30 (carbon fiber reinforced). This material is expensive, I only charge the additional costs for this material. Because the PEEK gearwheel is a much harder plastic, the motor sounds different compared to the standard nylon gearwheel.
 Yamaha PW series broken gearwheel repair PA66 GF30
Yamaha PW series broken gearwheel repair PA66 GF30
The gears are available on Tindie:
Note that I cannot give any warranty, as I am not responsible for the weak design of the Yamaha mid drive motor. You should know that my gear wheel also may break when extreem overloaded, just like the original Yamaha gear wheel. But note that my gear wheel material is much stronger than the original Yamaha.

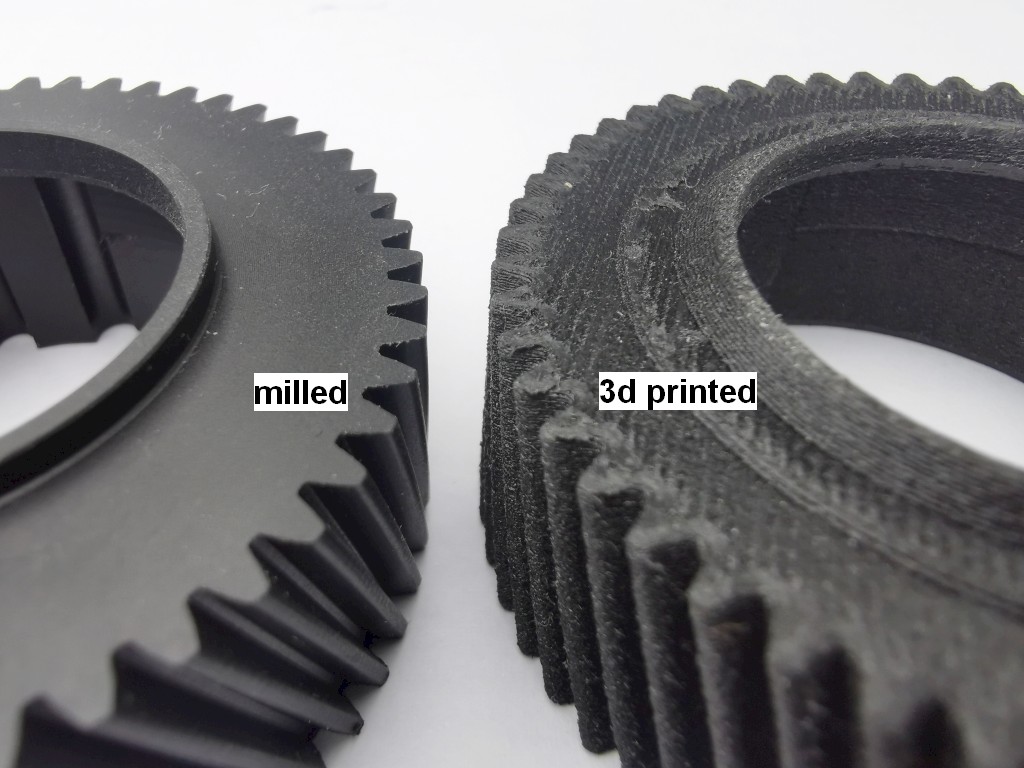 Note that my gearwheel is milled, NOT 3d printed
Note that my gearwheel is milled, NOT 3d printed
See also the article: Yamaha PW-X2 mid-drive motor tear down.

 Yamaha PW X2 gearwheel
Yamaha PW X2 gearwheel
Buy Bergquist thermal gap filler pads
The two pads with 1mm thickness can better be replaced when the printed circuit has been removed too. This is not necessary with the 3mm thick 10x10mm pads.
Together with the gear wheel you can order a thermal gap filler pad from 56mm x 23mm.
This is for the pads of 46mm x 23mm and 23mm x 10mm.
See more about the thermal gap filler pads here: Yamaha PW-X2 mid-drive motor tear down.
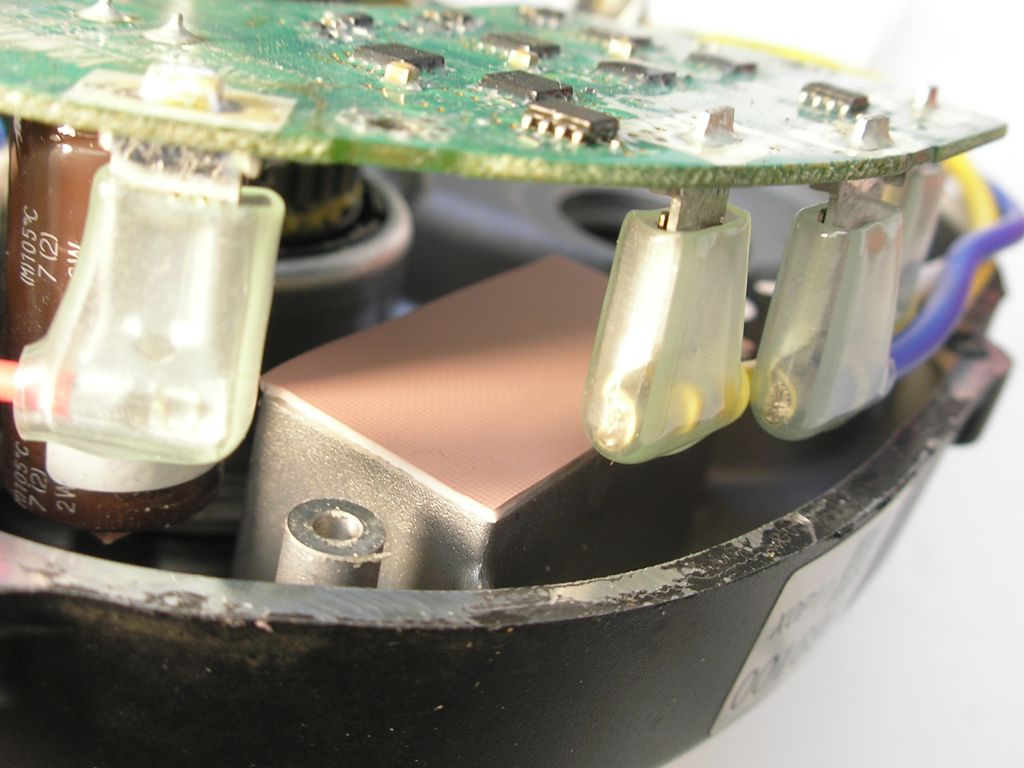 Stick the thermal pads to the motor housing
Stick the thermal pads to the motor housing
How to replace
Remove the broken gear and glue the new one in place. Use common one or two component PU polyurethane wood glue/adhesive. PU glue has been tested in practice and is very durable. Here polyurethane glue from Bison, note that the text may differ per country, as long as it is polyurethane then it is fine. Gorilla glue is also fine, is also polyurethane.
The clearance is approximately 0.1mm, this is to allow tolerances. If the gearwheel has more play, fill it with four strips of adhesive tape, 3 mm wide, evenly distributed around the circumference. Make sure the gear remains properly centered. Then glue it as described.
You can always remove my gearwheel by heating it up a little with a heatgun, which will soften the glue.
 Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear repair
 Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear repair
 Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear
Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 broken gear
Lubrication
To lubricate the gear wheel, you can apply the excess grease that can be found anywhere in the motor onto the gear wheel.
You can also use the Bosch gear grease drive unit.
How to avoid gear overload
Nylon gearwheels have an infinite lifespan when used properly: they are used successfully in hub motors where they rarely break. The problem, however, is that the Yamaha mid-drive motors have a design flaw that causes the maximum motor torque to be greater than the gear can withstand. In order to prevent a failure again, you will have to reduce extreme loads: namely driving at full throttle at low speeds, because than the motor torque is maximum.
The best solution would be a software update from Yamaha where the motor torque is automatically kept below a safe value.
Gearwheel breaks when the crank is blocked
The nylon gearwheel often breaks immediately when the crank is suddenly blocked while driving, for instance when you hit the ground with the pedal. The gear teeth break off due to the high kinetic energy of the fast rotating motor that transfers its energy to the gear. Perhaps Yamaha can prevent this by detecting the blocking with software and then immediately stop the motor via the Mosfets.
Save the nylon gear by reducing the maximum motor current
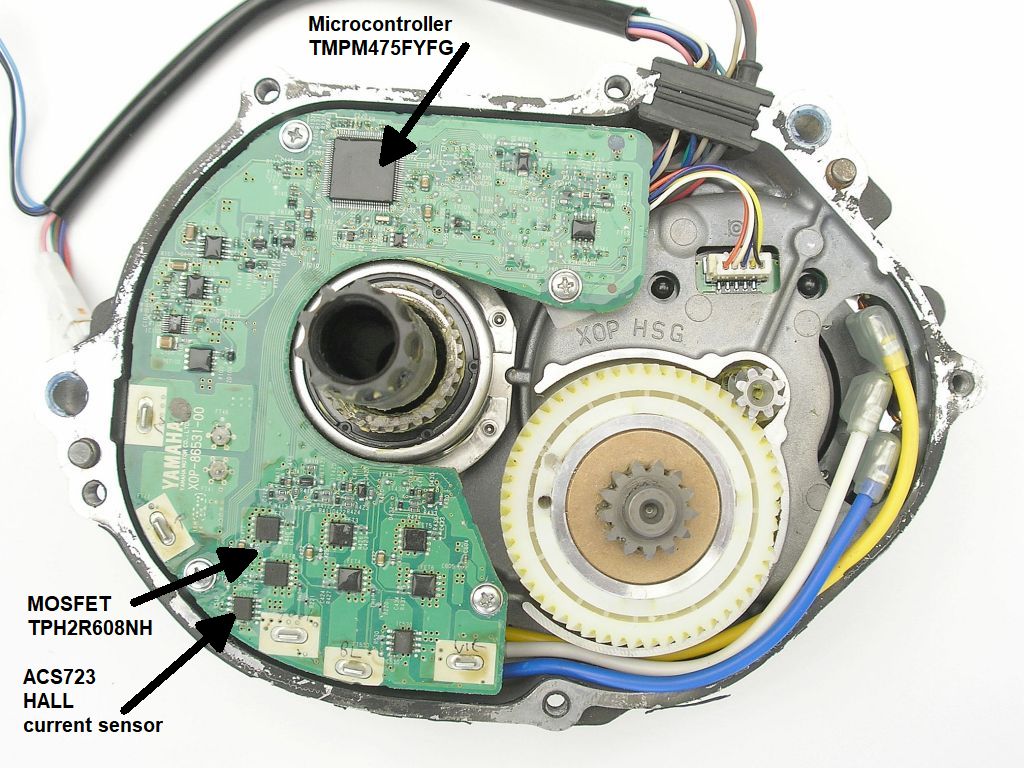
I have an idea how you could prevent the nylon gear from breaking again. The motor current is measured with Hall effect current sensors. Depending on the motor type, this is the 8-pin ACS723LLCTR-??AU (I don’t know the current version) or the 24-pin ACS709TLLF-45AB (this is 45A).
The solution is to reduce the maximum motor current by replacing the current sensors with lower current versions, for example, replace the ACS723LLCTR-40AU-T with the ACS723LLCTR-20AU-T.
Who would like to try this out?

Main Options Status Unpublished Category * - MotorRemove item Featured Featured NoYes Access Public Tags Type or select some tags Note Version Note





