Yamaha PW-X2 mid-drive motor tear down
- Yamaha PW-X vs PW-X2
- The benefits of the Yamaha PW-X2 mid-drive motor
- Yamaha PW X2 tear downYamaha PW-X2 facts
- Yamaha PW-X2 tear down
- Zero cadence support with two freewheels
- Yamaha PW-X2 gearwheels
- Freewheels
- Tuning the Yamaha PW-X2 motor for more power
- Broken Yamaha PW-X2 nylon gearwheel repair
- Yamaha PW-X2 electronics
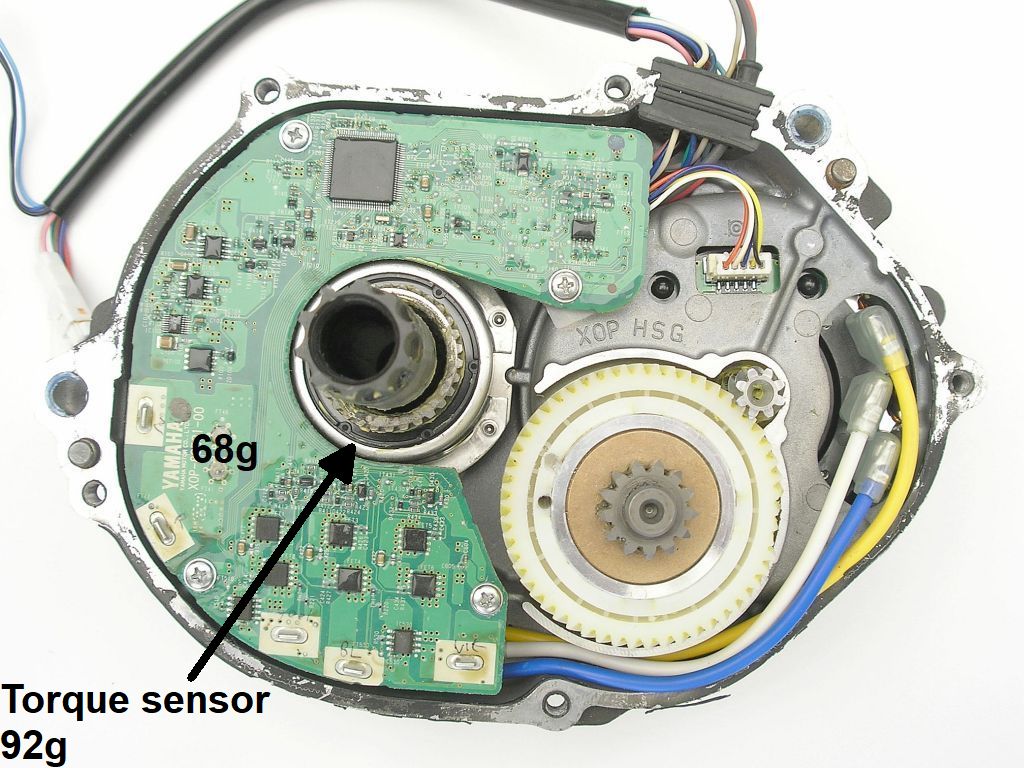
- Torque sensor board
- Yamaha motors with CAN bus
- Thermal gap filler pads
- Replace the thermal gap filler pads
- Liquid gasket
- Yamaha connectors
- Forums
Yamaha PW-X vs PW-X2
As far as I know, the mechanics of Yamaha PW-X2 is almost the same as the Yamaha PW-X. So everything that is told here also applies to the PW-X version. This motor is also used by Giant but strangely enough has a massive bottom bracket:
 Giant DyncDrive Yamaha PW-X2 motor with solid bottom bracket
Giant DyncDrive Yamaha PW-X2 motor with solid bottom bracket
The benefits of the Yamaha PW-X2 mid-drive motor
For my solar bike, I want to use the best mid-drive motor. My choice is the Yamaha PW-X2 motor for the following reasons:
- Zero cadence support
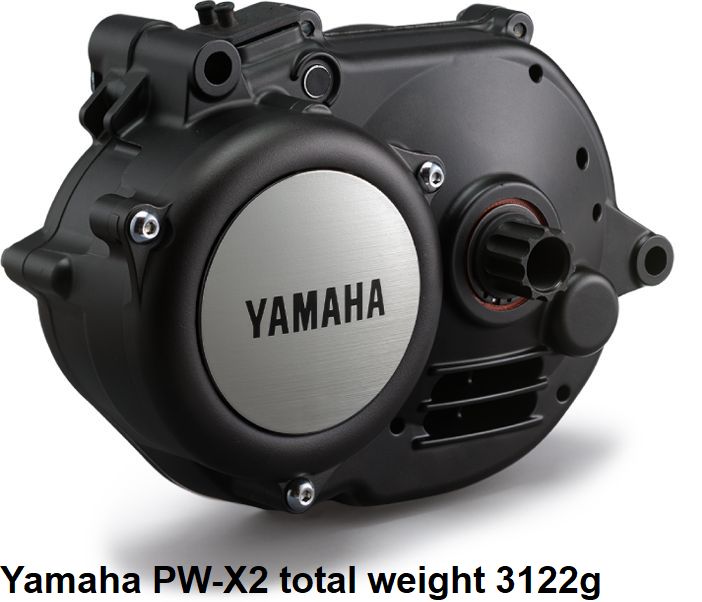
- Relatively low weight of 3.122 kg
- Any battery can be used on the Yamaha PW-X2 (with a hack)
- The efficiency of the Yamaha PW-X2 motor is the highest of all mid-drive motors 1*)
1*) This is due to the large gear ratio. The internal motor therefore has a high speed. Read more in this article.
 Yamaha PW X2 tear down
Yamaha PW X2 tear down
Yamaha PW-X2 facts
- Max. 250W
- Max 70Nm
Yamaha PW-X2 tear down
Zero cadence support with two freewheels
Most mid-drive motors (like the Bosch) have just one freewheel, this is used for pedaling without turning the motor. With just a single freewheel, the motor can never drive the rear wheel without the pedals turning, this requires an extra freewheel.
The Yamaha has 2 freewheels, so we can do both:
- Pedaling without turning the motor
- The motor can drive the rear wheel without the pedals turning
A disadvantage of the Yamaha is that gear wheel 3 and 4 will rotate during pedaling without motor assistance, which will give some loss.
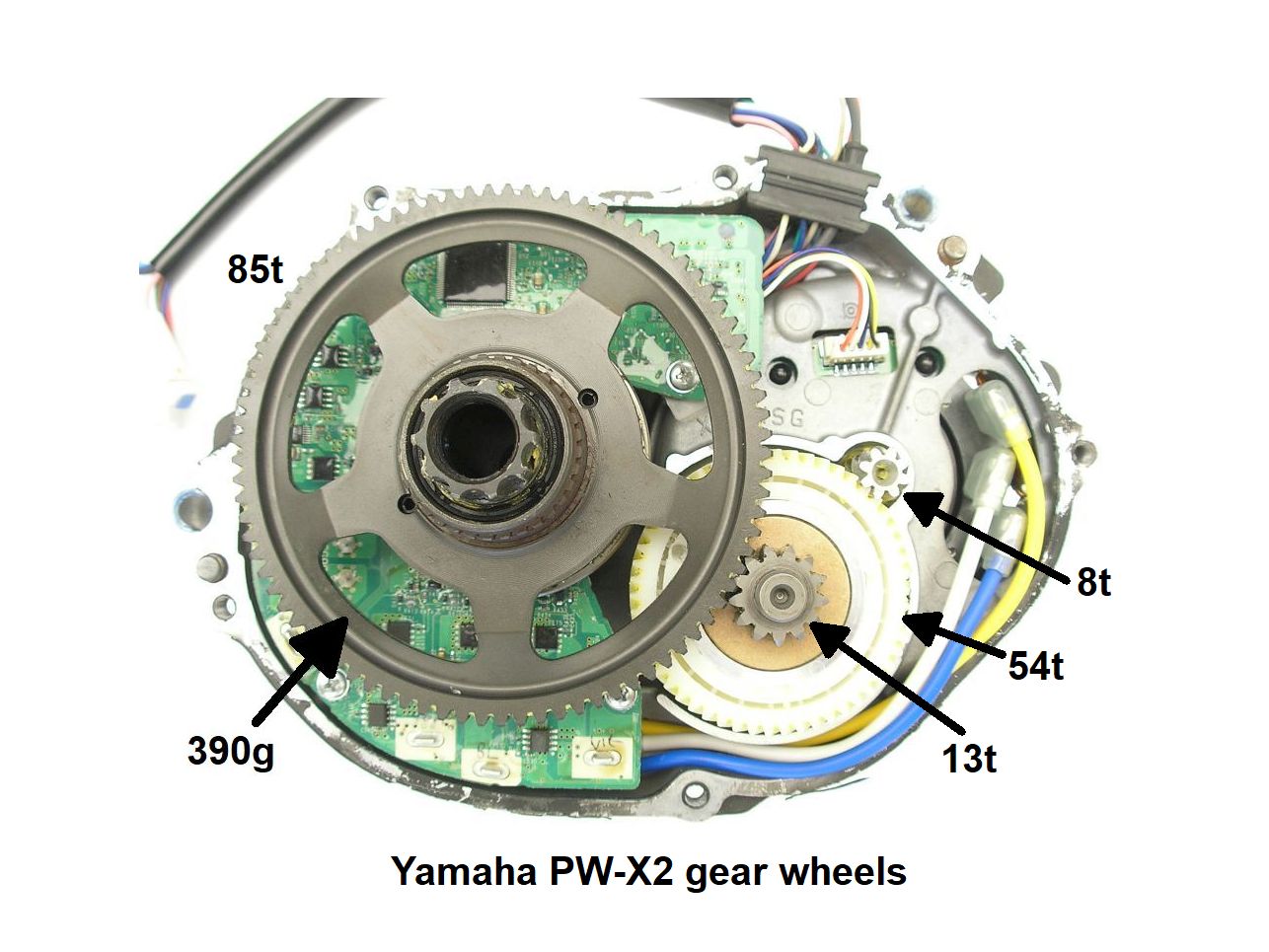
Yamaha PW-X2 gearwheels
| Gear 1 | Gear 2 | Gear 3 | Gear 4 | |||||||
| Material | steel | Material | nylon | Material | steel | Material | steel | |||
| Teeth number | 8 | Teeth number | 54 | Teeth number | 13 | Teeth number | 54 |
Gear1 85t, module 1.25, width 9mm
Gear2 13t
Gear3 54t, helical 20º, normal module 1, nylon, width 20mm
Gear4 8t
The gear ratio is 85/13 * 54/8 = 44.13
The motor speed of the Yamaha PW-X2 at a cadence of 100 is 4413 rpm.
Freewheels
Freewheel1 56mm
Freewheel2 32mm
Tuning the Yamaha PW-X2 motor for more power
The Yamaha PW-X2 motor has room for thicker copper wire. Rewinding the motor with thicker copper wire gives a little higher motor efficiency and therefore a higher permissible power.
 Tuning the Yamaha PW-SE motor for more power
Tuning the Yamaha PW-SE motor for more power
Broken Yamaha PW-X2 nylon gearwheel repair
I had nylon gears fabricated to repair the Yamaha PW-X and PW-X2 motor, see here.
As with the Yamaha PW-SE, the nylon gear is a weak part of the motor. It is definitely a design flaw as the gear wheel apparently cannot withstand the maximum force of the motor as it breaks too often. When the motor is broken, it will just be exchanged by Yamaha. Outside the warranty period, this will cost around $750. This is a big problem because, when the gear will be overloaded again, you can keep going this way.
The Yamaha motor has too much torque, which is the cause of the gear failure. Maybe it can be remedied by limiting the motor current. To do so, change the circuit with the ACS723 HALL current sensor (I have not tried this).
 Yamaha PW X2 broken nylon gear
Yamaha PW X2 broken nylon gear Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
 Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
 Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X2 broken gear repair
Yamaha PW-X2 electronics
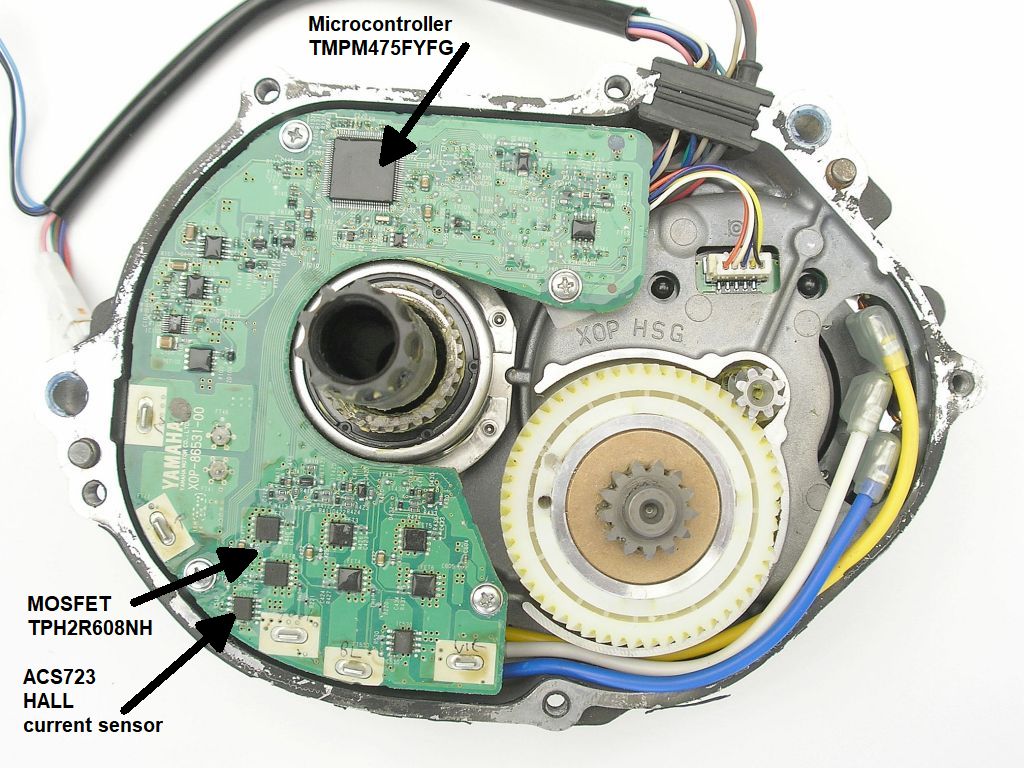
32 bit ARM Microcontroller TMPM475FYFG
- 256kByte flash, 18kByte RAM
- High-performance microcontrollers for brushless DC motors control with position sensing for sensorless commutation. Fast 1us 12-bit ADCs for current sensing with a high-speed PWM.
- CAN controller
IC510
ACS723 HALL current sensor
IC430
- L6387ED
- High voltage high and low-side driver
Power MOSFETs
- TPH2R608NH
- RDS(ON) = 2.1 mΩ
- 75V 150A
Torque sensor board
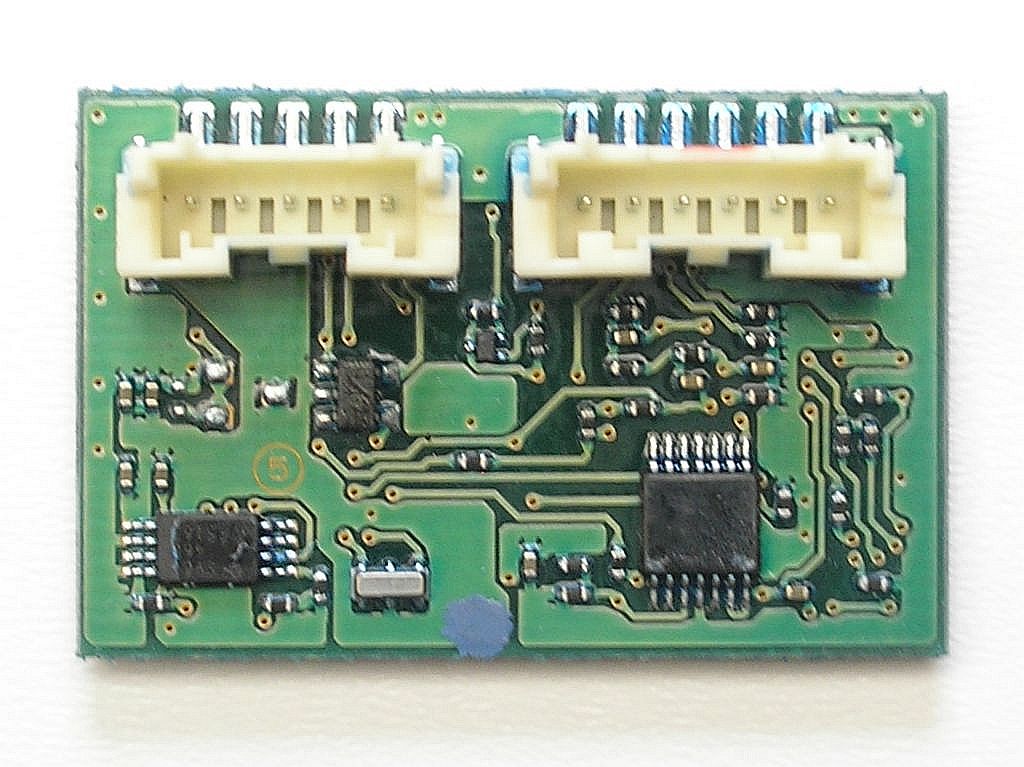
Yamaha motors with CAN bus
Note that Giant ebikes have a special version Yamaha motor, named Syncdrive, with a CAN-bus instead of the one wire bus.
Thermal gap filler pads
Take care of the thermal gap filler pads. There are two different thicknesses, the 1mm pads can better be replaced when the printed circuit has been removed.
Replace the thermal gap filler pads
I have looked if there are thermal pads which do not always have to be replaced after repairing the motor. The thermal pad must be elastic and has to rebound to the original shape after the pressure is removed. The Bergquist Gap Pad TGP 1000VOUS meets these requirements. The viscoelastic nature of the material also gives excellent low-stress vibration dampening and shock absorbing characteristics. The required thickness is 1mm for both the Bosch and Yamaha mid-drive motors. The thermal conductivity is 1 W/mK with 1mm.
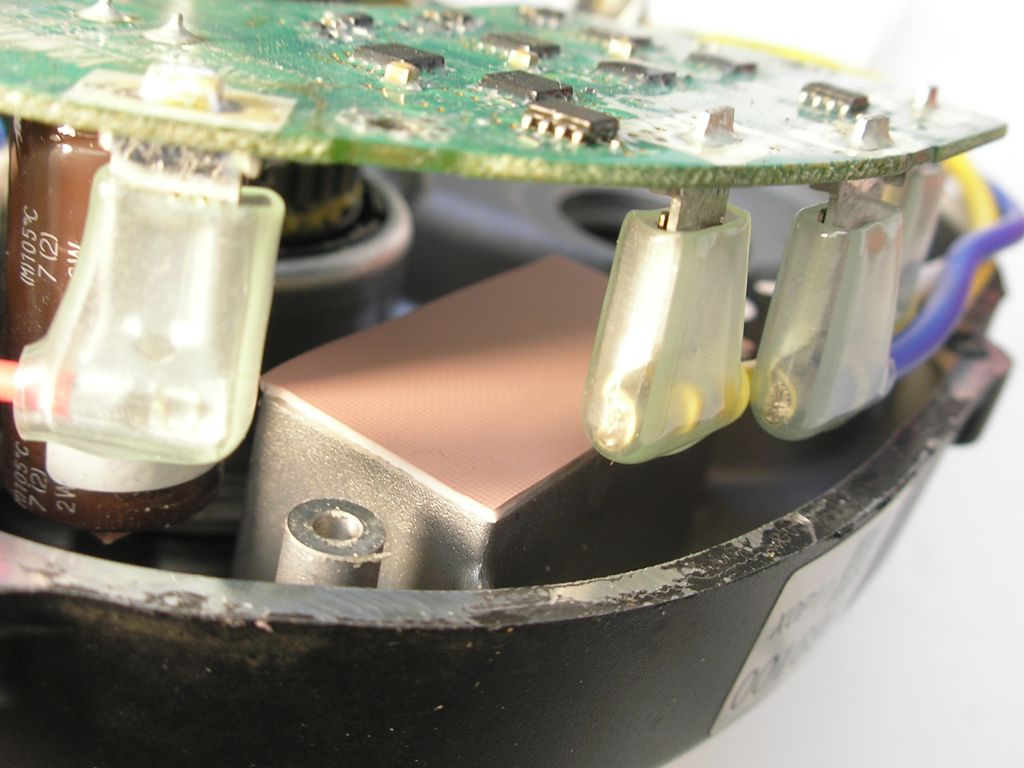 Replacing the thermal pads with Bergquist Gap Pad TGP 1000VOUS
Replacing the thermal pads with Bergquist Gap Pad TGP 1000VOUS
Liquid gasket
Attention: the Yamaha uses liquid gasket. Once the motor has been opened, this must be renewed.
Yamaha connectors
Yamaha use these connectors for the PW-SE mid-drive system:
JST JWPF series
 JST JWPF 2mm pitch wire to wire waterproof connectors
JST JWPF 2mm pitch wire to wire waterproof connectors
Hirose HR30 series
 Hirose HR30 IP68 compact waterproof connectors
Hirose HR30 IP68 compact waterproof connectors
Forums
https://www.pedelecforum.de/forum/index.php?threads/yamaha-pw-se-mid-drive-motor-tear-down.63476/
https://endless-sphere.com/forums/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=100440